The Canada Pension Plan (CPP) and Old Age Security have recently undergone changes that may affect when individuals begin drawing on these programs. The contribution period for CPP has been extended to age 70, and starting in 2024; individuals will have the option to contribute an “upper earnings limit,” equal to 114% of their yearly maximum pensionable earnings. However, it is essential to note that drawing CPP before age 65 will result in a reduction of .6% for each month before age 65.
For example:
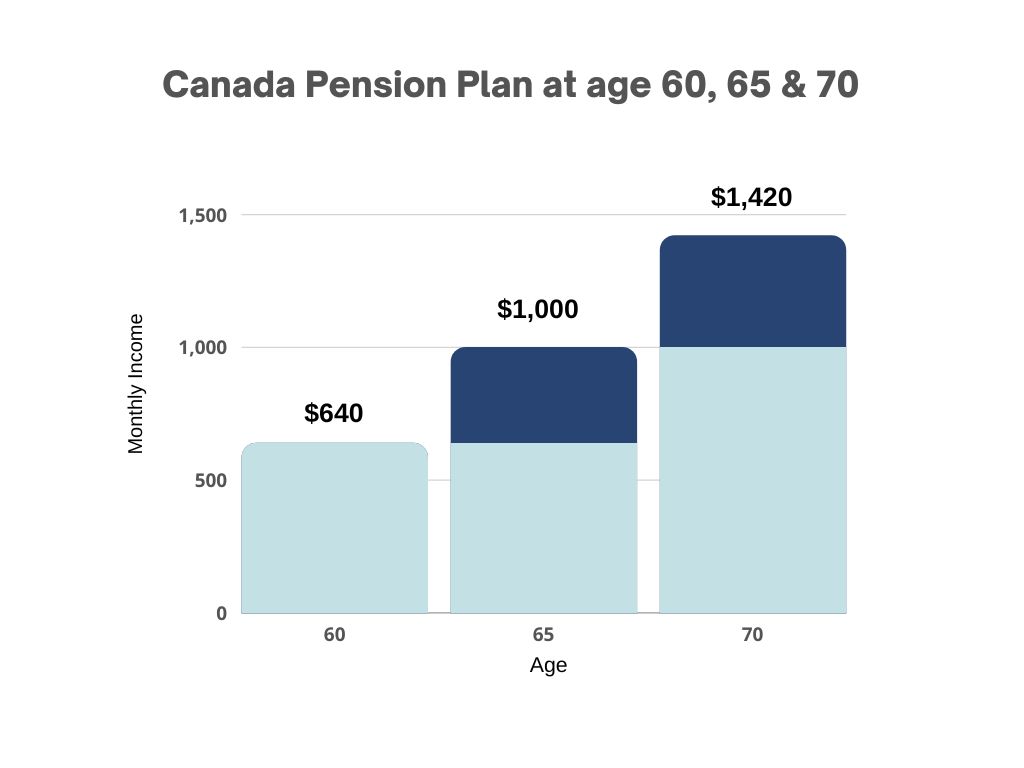
Early CPP: Drawing CPP at age 60 will result in a 36% reduction in benefits compared to waiting until age 65. It is also worth noting that if you continue working past age 60, you will still be required to contribute a minimum of 5.95% up to your yearly maximum pensionable earnings, which will be taxed at your marginal tax rate.
Late CPP: On the other hand, delaying the drawing of CPP until after age 65 will result in an increase of .7% per month until age 70, a potential increase of 42% in benefits.
The chart shows the variations in monthly income for these benefits based on the age at which they are received. (Please note we utilized a CPP starting value of $1,000 for simple math.)
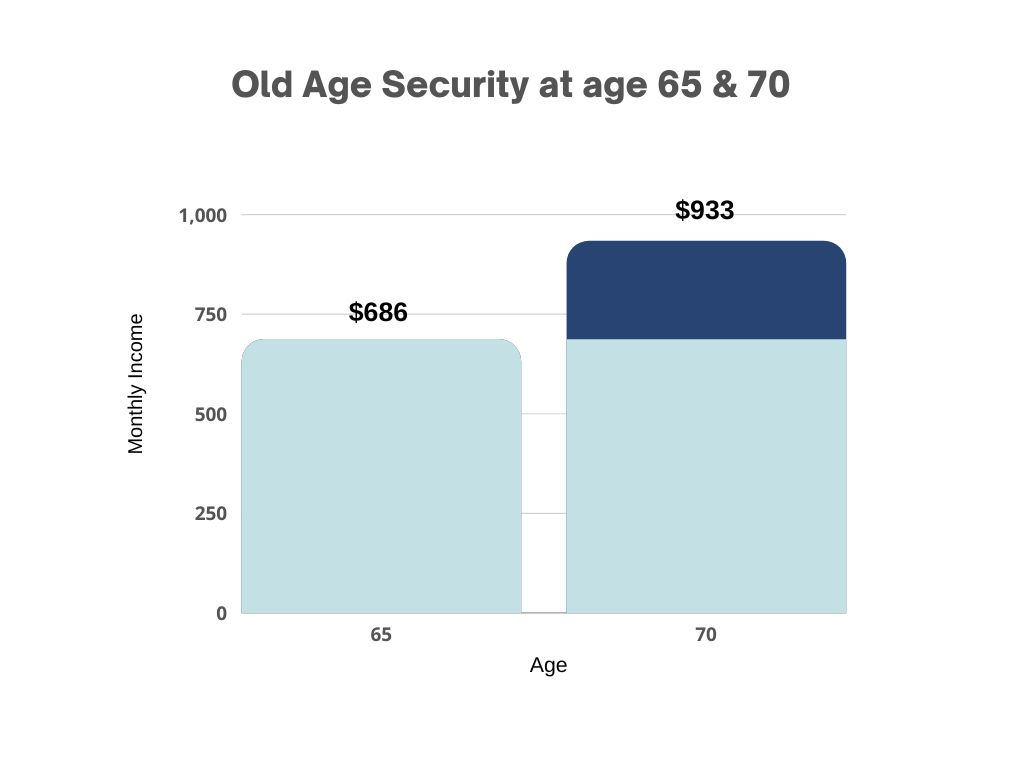
Old Age Security (OAS) is a non-contributory government benefit that begins at age 65 and is adjusted quarterly to account for inflation. OAS can be deferred until age 70 for an additional .6% per month, up to a maximum of 36%. Starting at age 75, OAS beneficiaries will receive an additional 10% in income.
Similar to CPP, OAS is taxed at the beneficiary’s marginal tax rate. However, as inflation and lifespan increase, it may make sense for some individuals to defer drawing on these benefits until later.
The chart below illustrates the difference in OAS monthly income for these benefits at different ages.
Don’t forget to consider the impact of inflation and longevity on your retirement planning. Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your savings and income over time, which means that the same amount of money may not go as far in the future as it does today. Longevity, or the increasing life expectancy of individuals, also means that you may need to plan for a longer retirement. This can impact the amount of savings you need to have and the timing of when you start drawing on retirement benefits such as CPP and OAS. Review these factors when deciding when to start receiving these benefits and to review and adjust your retirement plan as needed regularly.
It is essential to carefully consider your options and determine the best course of action for your personal situation. If you have any questions or want to discuss your options in more detail, please don’t hesitate to reach out for guidance.





